Html documentation
The three pillars of writing good CSS
- Responsive design
- Fluid layouts
- Media queries
- Responsive images
- Correct units
- Desktop first vs mobile first
- Maintainable & scalable code
- Clean
- Reusable
- How to organize files
- How to name classes
- How to structure HTML
- Web performance
- Less http requests
- Less code
- Compress code
- Use a CSS pre‐processor
- Less images
- Compress images
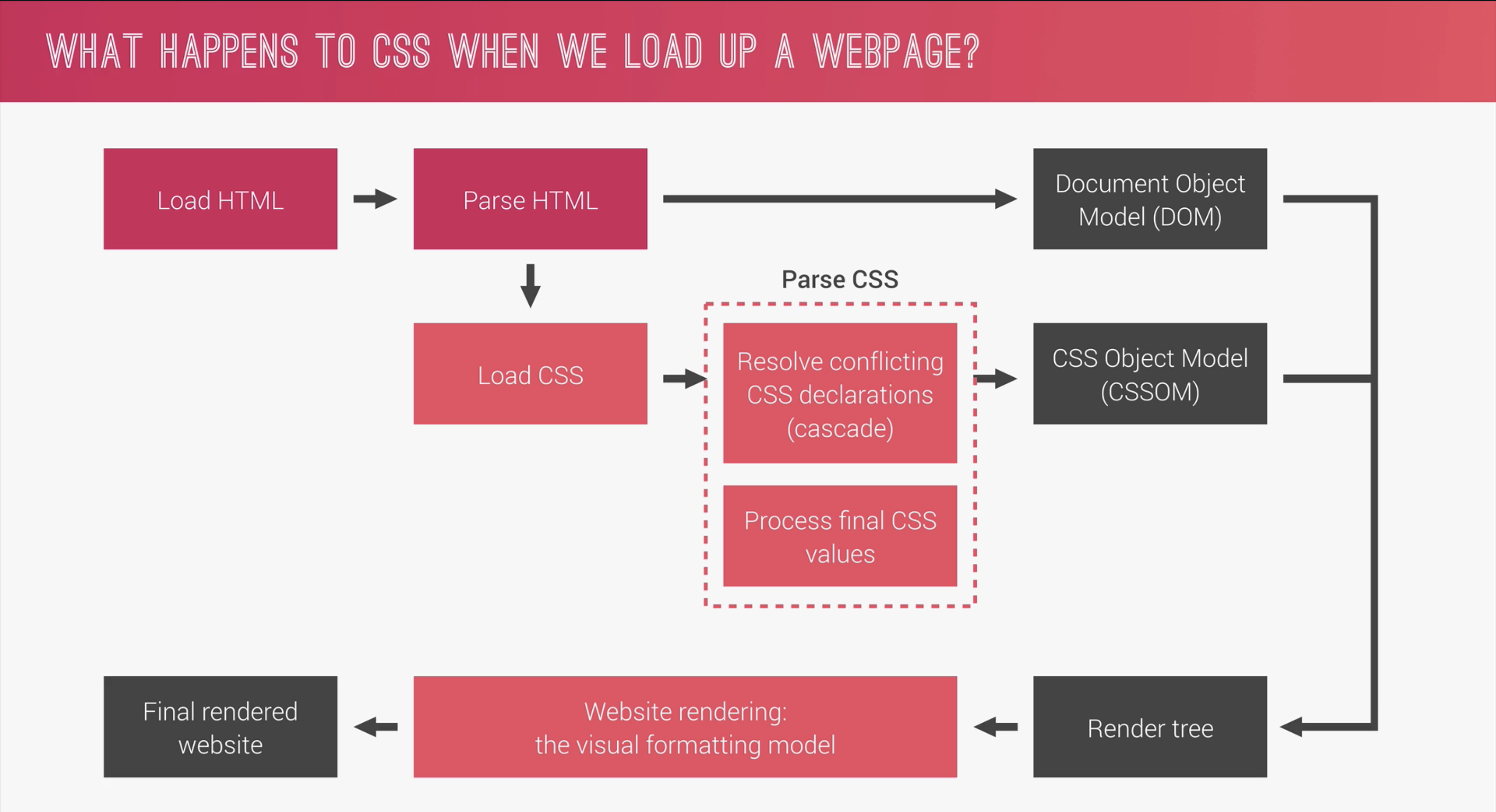
What happens when we load a webpage?
Http requests
HTTP stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol. Is it what happens when you access a website. Fetching data from web servers.
Http process
Someone enters a URL in the web browser, the computer then requests data from servers and the server sends back code. Finally the browser turns the code into human readable website.
Html basics
Divs & spans
<div>is a block level elements that group content together. Div means 'divisional elements'.<span>is an inline level elements that group content together.- In Elementor, each section is a section element, then each column is a div. If a section only has one column, no section element is needed, just a div.
Hr, br, sup & sub
<hr>is a horizontal rule with no closing tags. Create a line or a divider between elements. HR is a block level element.<br>is break in line. Pushing text to the next line, very rarely used.<sup>means superscript. It makes text elevated off the base line, for example, x2 (squared).<sub>means subscript. It makes text rendered below the base line, for example, for molecules H2O.
HTML Entities
HTML entitites start with & and finish with a ; They are special characters like roman numerals (Ⅰ), ampersand (&) signs or copyright (©) signs.
& = &
Here is a full list of html entities.
Html semantics
Semantics are divs with meaningful names, they act exactly like a div, but the names give meaning to what they are such as, main, section, header, footer, article, nav. Read more about semantics here;
<aside>
<details>
<figcaption>
<figure>
<footer>
<header>
<main>
<mark>
<nav>
<section>
<summary>
<time>
Html tables
Tables: Tr, td & th elements
<td>= Table data (table cell)<tr>= Table row<th>= Table header
Table header, footer & body
<thead>= Table header<tbody>= Table body (main content)<tfoot>= Table footer (totals/sums etc)
Colspan & Rowspan
colspan= "2"= An attribute to say how many columns the cell should span acrossrowspan= "2"= An attribute to say how many rows the cell should span across.
Table Example
Heaviest Birds
| Animal | Average Mass | Flying Bird | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kg | lbs | ||
| Ostrich | 104 | 230 | No |
| Somali Ostrich | 90 | 200 | No |
| Wild Turkey | 13.5 | 28.8 | Yes |
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th rowspan=
"2">Animal</th>
<th colspan=
"2">Average Mass</th>
<th rowspan=
"2">Flying
Bird</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Kg</th>
<th>lbs</th>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>Ostrich</td>
<td>104</td>
<td>230</td>
<td>No</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Somali
Ostrich</td>
<td>90</td>
<td>200</td>
<td>No</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Wild
Turkey</td>
<td>13.5</td>
<td>28.8</td>
<td>Yes</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
Html forms
When we submit a form, a HTTP request is sent, we can control where the form goes to with the action attribute. We can also control which type of HTTP method is used. (Get/Post)
Key attributes to mention
- Name is an attribute for inputs. It names the input data to send to the server, so name the input relevant to what the input it. This should go on every single input used.
- Value is an attribute for radio buttons. The value sends through what the value is selected to the server.
<form action="">
<div>
<label for=
"username">Enter your
username</label>
<input id=
"username"
type=
"text"
placeholder=
"Username"
name=
"username">
</div>
<div>
<label for=
"password">Enter your
password</label>
<input id=
"password"
type=
"password"
placeholder=
"Password"
name=
"password">
</div>
<button>Submit</button>
</form>
Hijacking Youtubes search
More inputs
Form validations (browser validations)
The following attributes are common browser validations;
- required Make the field required.
- min-length Add a minimum input length (great for passwords).
- maxlength Add a maximum input length (great for passwords).
- pattern Each validation follows a pattern, for example, email needs an @ symbol, with the pattern attribute, we can specify a pattern to follow for validation of specific fields.
SVGs
SVGs should be used instead of icon fonts as icon fonts has a lot of issues and can render black squares. Icon fonts are also not accessible to screen readers.
To use basic SVGs with sprite files;
Sprite files are svg files with all of the svg's in 1 file that is downloaded from a library. Sprite files are best practice to use as only 1 http request is needed instead of 1 for each svg.
- Find an svg library like Icomoon.io
- Download the svg's from the library
- To include svg's with sprite files, do the following;
<svg>
<use
xlink:href="img/sprite.svg#icon-maginfying-glass"><use>
</svg>
The xlink:href attribute only works on web servers.
List of sources
- Colt Steeles web
developer bootcamp 2021